Electrical fires are one of the top causes of fires in industrial settings. In fact, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) found that fires caused by electrical distribution and lighting equipment accounted for 55% of direct property damage, as well as 9% of civilian injuries from 2011 to 2015. Electrical failure or malfunction caused $25 million dollars of direct property damage in the same time span.When a Class C fire occurs, it's important to know which fire extinguisher or suppression system is appropriate. How do electrical fires start? How do you fight an electrical fire? Let's dive into the answers.
What is a Class C Fire?

Fire is categorized into five different types: A, B, C, D, and K. Each type of fire feeds on a specific fuel source and is dealt with using a specific type of fire extinguisher or fire suppression system. For example, Class A fires are the most common type of fire and come from materials like wood, paper, fabric, rubber, and plastic. Water and foam extinguishers are most often used to fight Class A fires. However, Class C fires are electrical fires and a specific fire suppression system is needed.
Class C fires use live electrical currents or electrical equipment as a source of fuel. A Class C fire can involve electrical tools, wiring, or appliances, and often occur in industrial settings. Keep in mind that Class C fires cannot be fought with water— using water as an extinguishing agent can actually make Class C fires worse! The most effective way to put out a Class C fire is to isolate the source of electricity and use a Class C fire extinguisher.
What is an Example of a Class C Fire?
A Class C fire can start from a variety of ignition sources, like:
- Electrical power or utility lines
- Electrical service supply wires from a utility electric meter or meter box
- Wiring from meter box to circuit breaker panel board, switchboard, or circuit breaker board
- Electrical branch circuit
- Outlet or receptacle wall switch
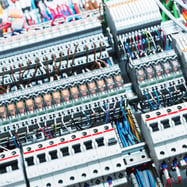 However, there are some places where Class C fires are more common. A Class C fire can start in an electrical cabinet. Control cabinets and relay panels have many electrical connections and ignition points. Faulty wiring or short circuits can cause an electrical panel to ignite and spread unless action is taken. The result can be devastating, causing injury to workers, damaged equipment, and lengthy (and costly) downtime.
However, there are some places where Class C fires are more common. A Class C fire can start in an electrical cabinet. Control cabinets and relay panels have many electrical connections and ignition points. Faulty wiring or short circuits can cause an electrical panel to ignite and spread unless action is taken. The result can be devastating, causing injury to workers, damaged equipment, and lengthy (and costly) downtime.
Despite the fact that electrical panels have many potential ignition points, fire protection for electrical cabinets is not always a regulatory requirement.
Which Fire Extinguisher is Used for Class C Fires?
There are a few types of fire protection systems to fight Class C fires. Options include Carbon Dioxide (CO2), clean agent fire suppression systems, and FlexRopeTM.
Carbon Dioxide is an electrically non-conductive gas that can easily suppress a Class C fire. However, CO2 fire suppression systems are not always fit due to environmental concerns and occupied space requirements.
Clean agents like FM-200™ and FK-5-1-12 are fast and effective solutions to Class C fires, are safe in occupied spaces, and do not leave residue.
Another way to protect electrical panels is FlexRope™. This easy-to-install, zero maintenance solution is specifically designed for electrical panel and cabinet fire protection. The FlexRopeTM reacts to an electrical fire by releasing an aerosol to suppress the fire.
All in all, electrical fires are unpredictable. Buy by taking preventative measures, Class C fires don't have to be catastrophic.

